How to Create Graphs¶
During chromosomal rearrangements, translocations may occur and graphing such a phenomenon is possible with gTrack. However, the edges parameter must be used. This vignette will explain how to prepare a graph.
Edges Parameter¶
In order to create a connected graph in gTrack, the edges parameter of gTrack must be supplied a matrix or a data frame of connections.
##create a GRanges object storing 10 sequences. These sequences will serve as nodes for the graph.
gr <- GRanges(seqnames = Rle(c("chr1" , "chr2" , "chr1" , "chr3") ,
c(1,3,2,4)), ranges = IRanges(c(1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19) ,
end = c(2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20),
names = head(letters,10)),
GC=seq(1,10,length=10),
name=seq(5,10,length=10))
gr
## GRanges object with 10 ranges and 2 metadata columns:
## seqnames ranges strand | GC name
## <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <numeric> <numeric>
## a chr1 [ 1, 2] * | 1 5
## b chr2 [ 3, 4] * | 2 5.55555555555556
## c chr2 [ 5, 6] * | 3 6.11111111111111
## d chr2 [ 7, 8] * | 4 6.66666666666667
## e chr1 [ 9, 10] * | 5 7.22222222222222
## f chr1 [11, 12] * | 6 7.77777777777778
## g chr3 [13, 14] * | 7 8.33333333333333
## h chr3 [15, 16] * | 8 8.88888888888889
## i chr3 [17, 18] * | 9 9.44444444444444
## j chr3 [19, 20] * | 10 10
## -------
## seqinfo: 3 sequences from an unspecified genome; no seqlengths
## Specify links between nodes using a matrix. Numeric 1s refer to a connection while conversely with 0s.
##create an N*N matrix filled with 0s.
graph = matrix(0 , nrow = 10 , ncol = 10)
##set certain indices to 1.
graph[1,3]=1
graph[1,10]=1
graph[2,5]=1
graph[2,8]=1
graph[3,5]=1
graph[4,1]=1
graph[4,2]=1
graph[4,6]=1
graph[4,9]=1
graph[5,1]=1
graph[5,2]=1
graph[5,4]=1
graph[8,1]=1
graph[8,2]=1
graph[9,1]=1
graph[10,1]=1
##use edges parameter to create graph.
plot(gTrack(gr , edges = graph , stack.gap = 5))
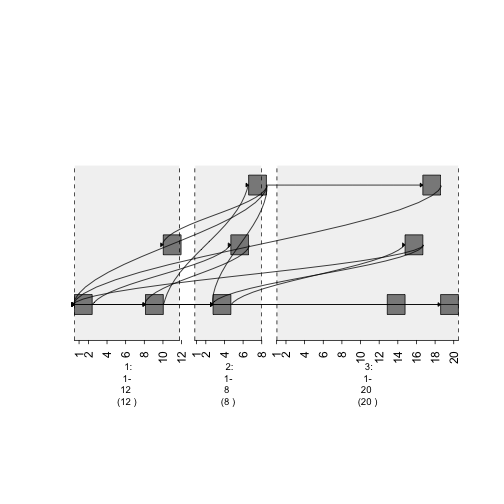
plot of chunk plot1
col Column¶
If a matrix is used to create a graph, color and style of edges cannot be specified.Instead of using a matrix, a data frame can be used to specify those attributes.
##the "from" column specifies the beginning node (range).
##the "to" column specifies the end node (range).
##the "col" specifies the color of the edge.
graph = data.frame(from = 1:9, to = c(6,9,7,2,4,10,8,5,3) , col = c('red', 'blue', 'green'))
plot(gTrack(gr , edges = graph , stack.gap = 5))
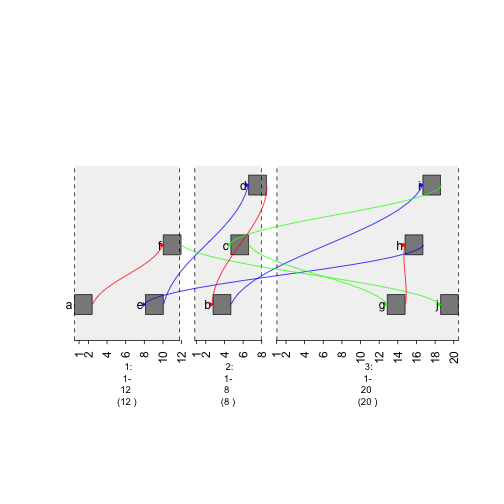
plot of chunk colored-graph
lwd Column¶
To change the width of the edges, use the lwd parameter.
##the "lwd" column specifies the width of the edge.
graph$lwd = 1.844941
graph
## from to col lwd
## 1 1 6 red 1.844941
## 2 2 9 blue 1.844941
## 3 3 7 green 1.844941
## 4 4 2 red 1.844941
## 5 5 4 blue 1.844941
## 6 6 10 green 1.844941
## 7 7 8 red 1.844941
## 8 8 5 blue 1.844941
## 9 9 3 green 1.844941
plot(gTrack(gr, edges = graph, stack.gap = 5))
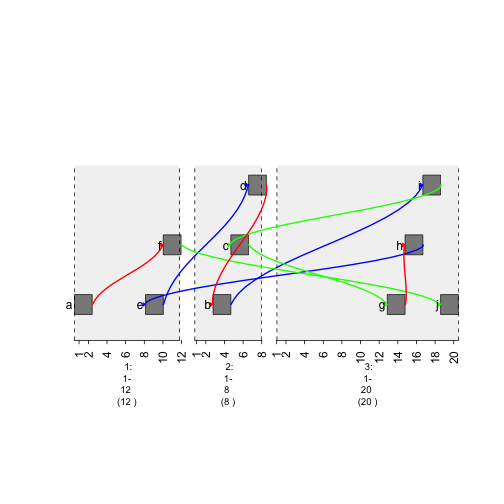
plot of chunk width-graph
lty Column¶
Change style of edge by lty parameter.
## lty specifies the style of the edge (no dashes, big dashes, little dashes)
graph$lty = c(1,2,3)
plot(gTrack(gr , edges = graph , stack.gap = 5))
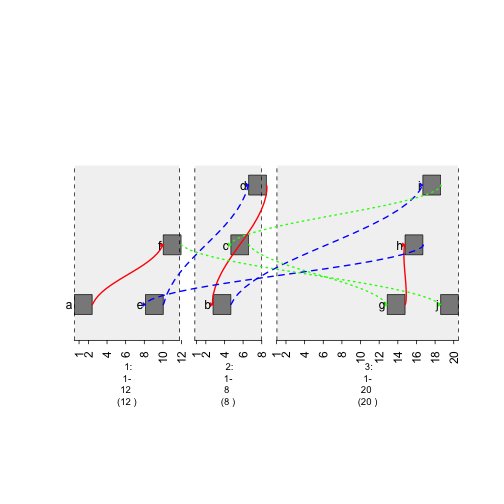
plot of chunk style-graph
h Column¶
Increase “curviness” of the edges by adding h column.
graph$h = 10
plot(gTrack(gr , edges = graph , stack.gap = 5))
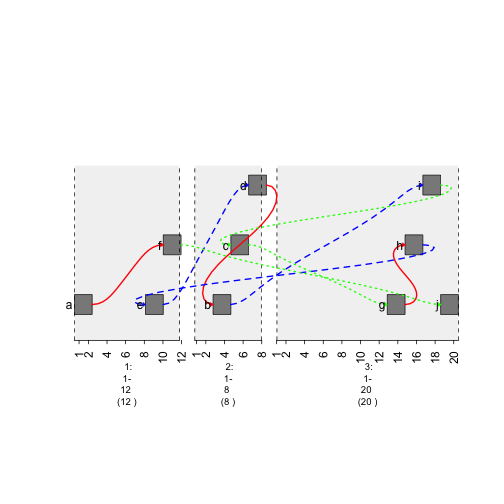
plot of chunk curviness-graph